-
주택
주택점유형태
-
주택점유형태
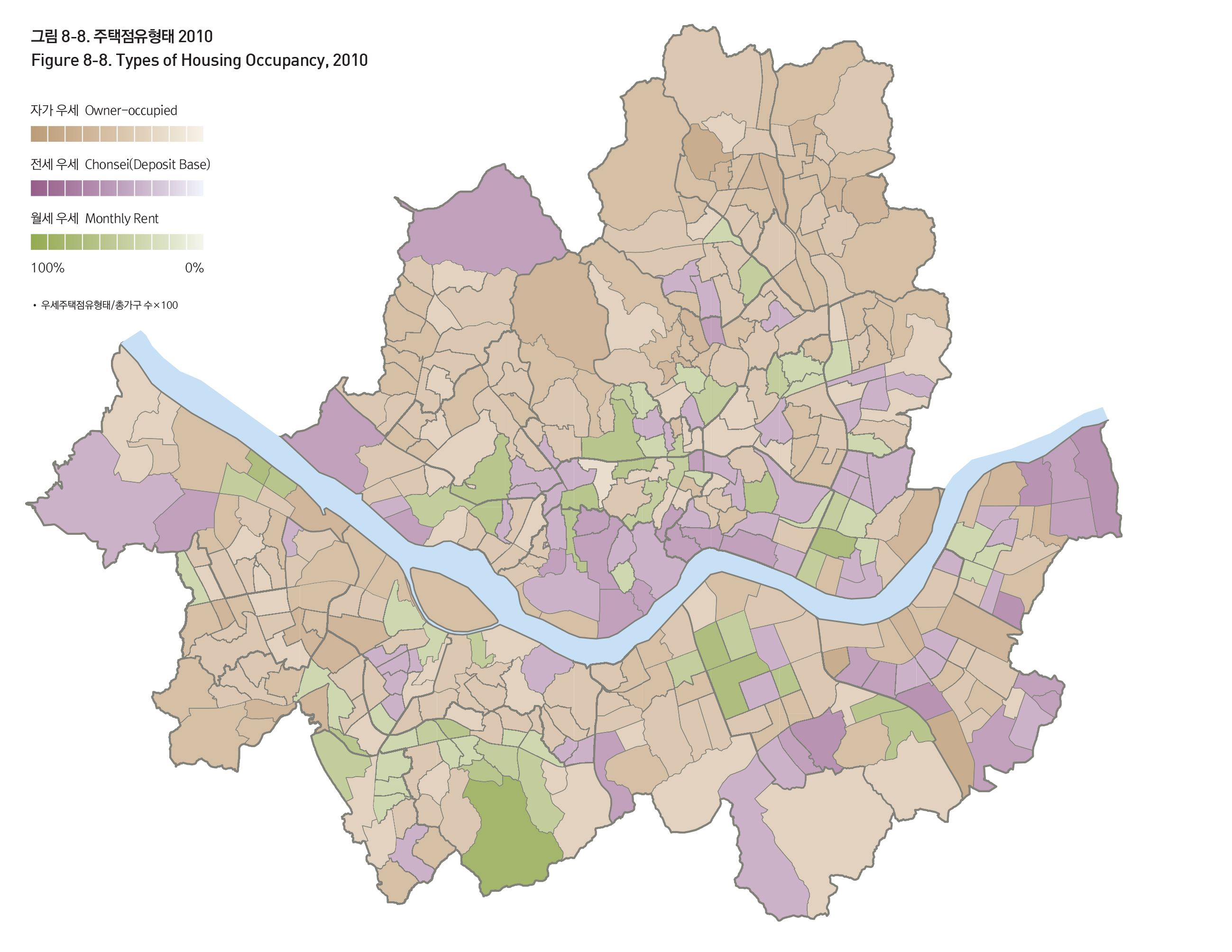
주택점유형태는 주택유형과 밀접한 관련을 갖는데, 아파트가 우세한 지역에서는 자가가구가, 단독 및 다세대, 연립이 우세한 지역에서는 전세가구가 우세하다. 다만 도봉구 수유지역, 은평구 등은 연립 및 다세대 주택이 우세하나 점유형태로는 자가가구가 우세하다. 월세가구가 우세한 지역은 단독세대가구가 많은 대학교와 고용중심지 등인데, 이는 이동성이 높은 젊은 학생과 단독가구의 특성 때문이다.
서울시민의 자가율(자기가 소유하고 있는 집에서 거주하는 비율)은 1960년 56.5%에서 지속적으로 증가하여 1980년대 중반까지 80%대를 유지하였으나, 90년대로 접어들면서 오히려 감소하여 2010년 현재 41.1%이다. 한편 월세 및 전세를 포함한 임차주택에 사는 비율은 1970년 10.1%에서 꾸준히 증가하여 2010년에는 57.5%에 달했다. 2000년 임차주택에 사는 비율이 33.0%에서 2010년 현재 57.5%로 급증한 이유는 부동산 경기 침체로 소유보다 임차를 선호하는 가구가 크게 늘었기 때문이다.
TENURE TYPE
The types of housing occupancy are strongly linked with the types of housing. Apartment-heavy areas tend to be owner-occupied, while areas where row houses are prevalent tend to be ‘Chonsei (deposit base)’. Areas with where ‘Wolsei (monthly rent)’ housing is dominant tend to be college areas or employment quarters with lots of mobile one-person households.
The owner-occupancy ratio rose steadily between the 1960s and 1980s, but scaled back from the 1990s onwards to reach 41.1% in 2010. In contrast, the ratio of rental or lease housing climbed consistently from 10.1% in 1970 to 57.5% in 2010. Its recent growth can be attributed to the real estate recession and the subsequent household tendencies to continue living on lease instead of buying.
출처 : 통계청, 인구주택총조사, 2010년
출처 : 통계청, 인구주택총조사