-
교통
도로시설
-
도로시설
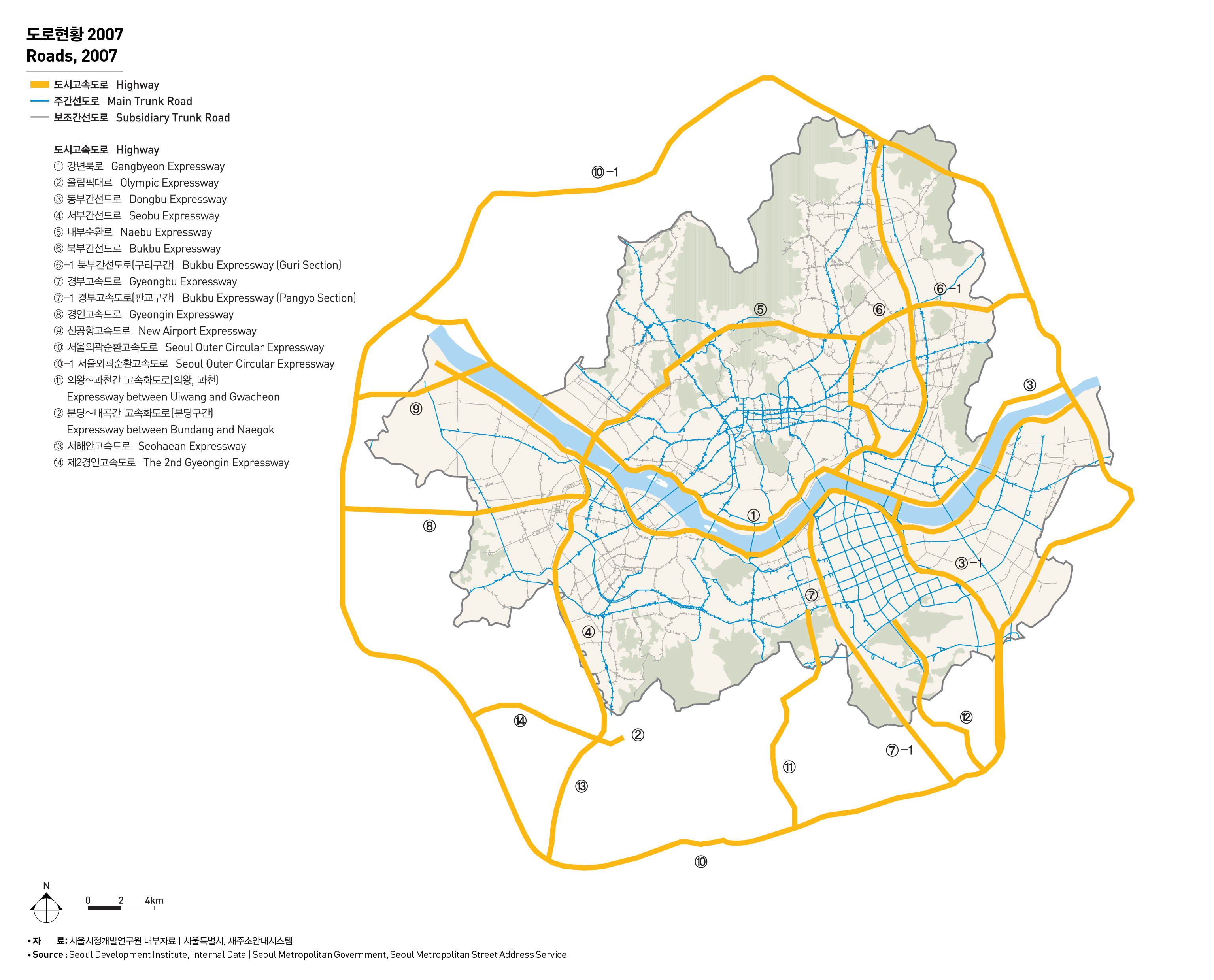
서울의 도로망은 방사형, 격자형, 순환형 도로들이 혼합된 형태이며, 이는 도시의 형성과정과 연관이 있다. 1930년대에는 4대문안과 마포, 영등포 등 일부 외곽지역에만 도로가 연결된 형태에서 점차 강북지역에 도로망이 형성되는 과정을 거쳐 1980년대에는 강남지역에 격자형 도로망이 발달되었으며, 1990년대 도시고속도로를 비롯한 간선도로 정비를 통하여 오늘에 이르고 있다.
서울의 도로망 체계에서 주요 교통흐름은 고속도로와 도시고속도로로 구성된 고속화도로, 주간선도로, 보조간선도로에서 담당하고 있으며 도로 연장은 각각 197.5Km, 245.8Km, 713.1Km(2007년 기준)에 달하고 있다. 도시내 기간망 역할을 담당하고 있는 도시고속도로 체계를 보면 외곽순환, 내부순환도로가 환상축을 형성하고 있으며, 강변북로와 올림픽대로가 동서방향의 간선축을 이루며, 동부간선, 서부간선, 그리고 최근 개통된 북부간선도로가 차량 이동의 중추기능을 담당하고 있다.
ROADS
Seoul’s road network shows a combination of a radial road, across stripe road and a ring-type road, and is related with the process of forming a city. Roads were connected in some outskirts such as Mapo and Yeongdeungpo as well as inside the Four Gates in 1930s, and the road network began to be built in the North of Han river. The cross stripe road network was developed in the South of Han river in 1980s, and trunk roads as well as highways have been improved since 1990s.
Seoul's traffic flow depends on highways, main trunk roads, subsidiary trunk roads, and the road extension rate stands at 197.5Km, 245.8Km and 713.1Km(as of 2007), respectively. Highway system serves as a backbone network of urban traffic, and the outer circular expressway and inner circular expressway form an outer ring. Dongbu Expressway, Seobu Expressway and newly built Bukbu Expressway play a vital role in traffic movement.
출처 : 서울시정개발연구원 내부자료
서울특별시, 새주소안내시스템