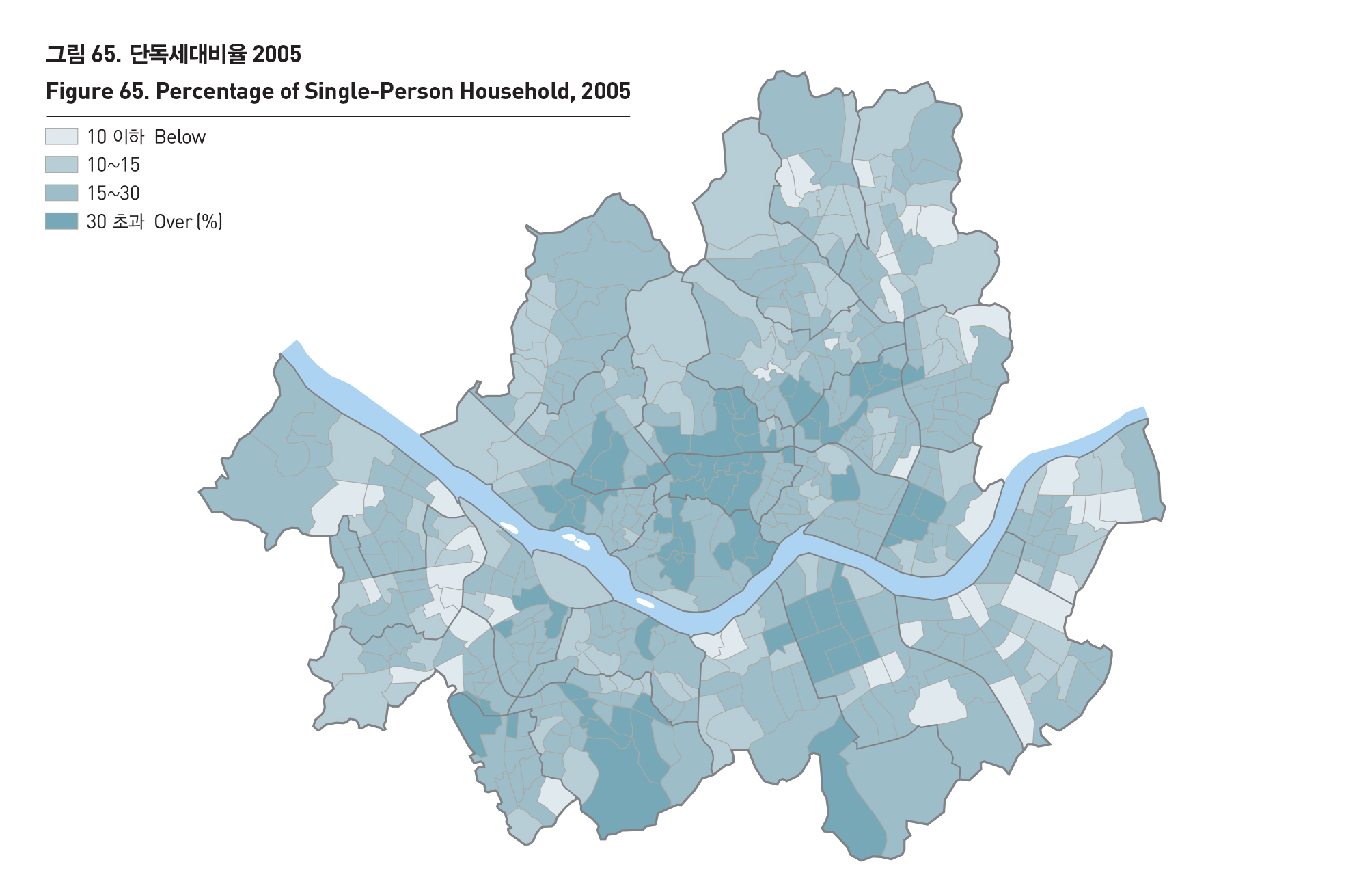
-
주택
주택점유형태
-
주택점유형태
서울의 2005년 주택점유형태는 자가 45%, 전세 33%, 월세 20%로 자가 보유가 가장 높은 비중을 차지하고 있는 가운데 월세의 비중도 증가하고 있는 추세이다.
주택점유형태는 주택유형과 밀접한 관련을 갖는데, 아파트가 우세한 지역에서는 자가가구가, 단독 및 다세대, 연립이 우세한 지역에서는 전세가구가 우세하다. 다만 도봉구 수유지역, 은평구 등은 연립 및다세대 주택이 우세하나 점유형태로는 자가가구가 우세하다. 월세가구가 우세한 지역은 단독세대가구가 많은 공단주변과 도심지로서 이동성이 높은 단독가구의 특성 때문이다. 서울은 대도시와 같은 슬럼현상은 나타나지 않고 있으나, 주택점유형태, 주택유형, 주택규모가 소득수준과 매우 높은 상관관계에 있으며, 주택유형 및 점유형태 등에 따른 거주지 분화현상이 나타나고 있다.
TENURE TYPE
Seoul’s housing tenure types are made up of 45% of home ownership, 33% of chonsei(lump-sum deposit only), and 20% of wolsei (monthly rent) as of 2005. The home ownership accounts for the biggest part of housing tenure types and the rate of wolsei (monthly rent) has been on the rise.
The housing tenure is closely related with housing types. For example, home ownership ratio is high in regions with many apartments, and the rate of chonsei is high in regions with many detached dwellings, apartment units in a private house and row houses. The exception is Suyu-dong of Dobong-gu and Eunpyeong-gu, where row houses and apartment units in a private house are more than apartments, but home ownership ratio is high. High rates of monthly rents are easily seen in regions adjacent to an industrial complex with many single-person households that often move to downtown. Unlike other large city, slums are rarely seen in Seoul, but there is a significant correlation between housing tenure type, housing types, the size of a house and income level, and differentiation of residential areas depends on housing type and housing tenure type.
출처 : 통계청, 인구주택총조사보고서, 2005