-
자연
바람
-
바람
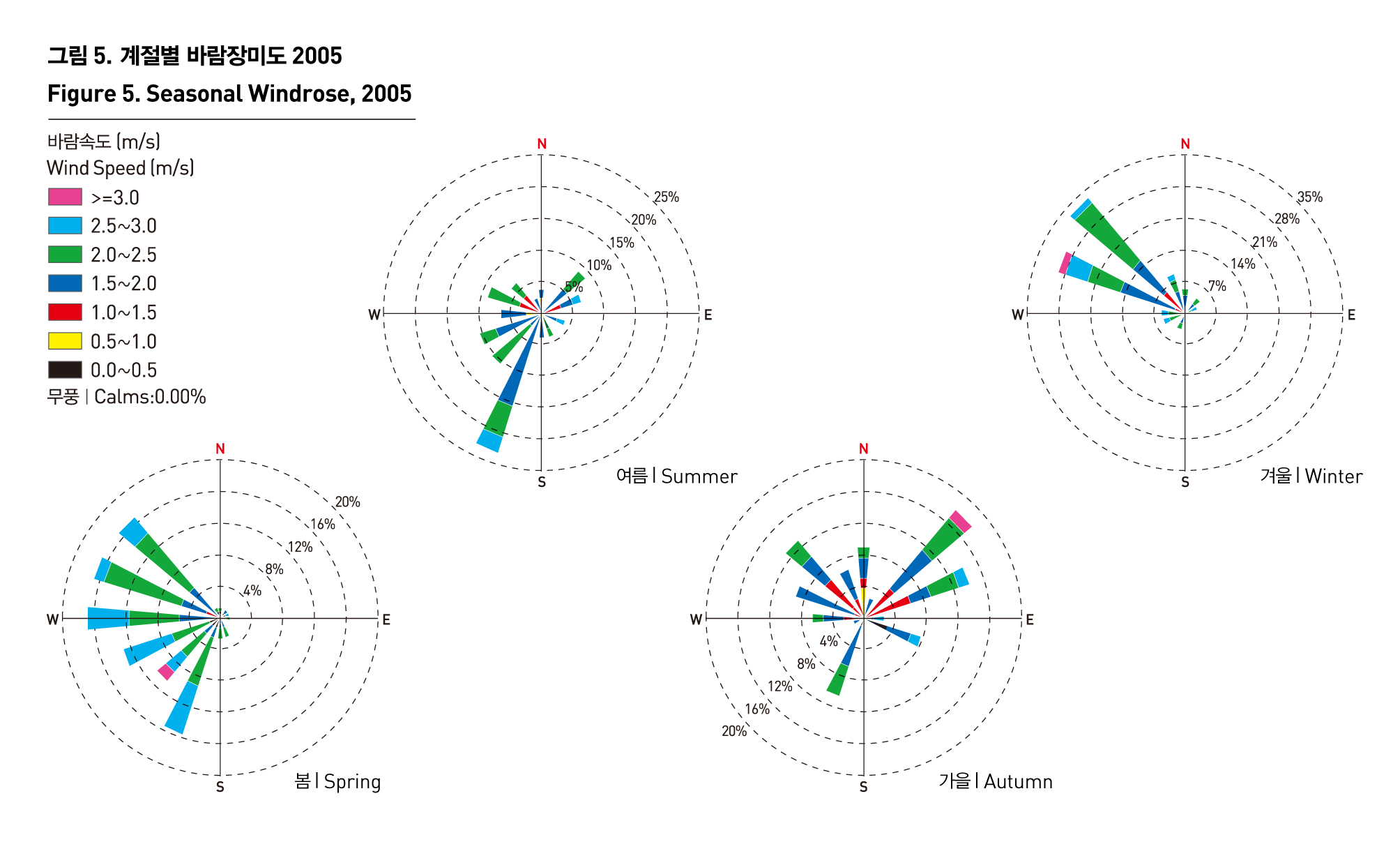
도시 내에서 바람의 방향은 오염물질의 이동과 밀접한 관련을 가지며, 바람이 정체되는 지역은 오염농도가 높아질 가능성이 있다. 2005년도 자동기상관측망(AWS)에서 관측된 자료를 보면 연평균 풍속은 1.9m/s이며, 3·4월에 바람이 가장 세게 불었으며, 10월의 바람이 가장 약한 세기를 나타낸다. 최다 풍향은 북서풍이며, 계절별로는 봄, 여름, 가을, 겨울 순서로 서풍, 남남서풍, 북동풍, 북서풍의 빈도가 높다. 2005년의 바람장을 계절별로 살펴보면 가을, 겨울에는 북서풍의 빈도가 높다.
서울의 바람은 한강을 따라 형성되는 바람장이 매우 우세하며, 한강의 지류인 중랑천, 탄천을 따라 바람이 이동한다. 중랑천을 따라 흐르는 바람은 도봉산, 아차산, 수락산에서 형성된 산골바람을 만나 상계동 지역에서 일부 와류현상을 보이고 있다.
WIND
The wind direction in a city is closely related with the movement of pollutants, and the pollution density is likely to grow where wind hardly blows. The data of AWS in 2005 shows an annual wind speed of 1.9m/s, and the wind speed is the highest in March and April, and the lowest in October. The northwesterly wind is the most common type of wind, and the west wind, south-south-west wind, northeasterly wind and northwesterly wind are a prevailing wind in spring, summer, autumn and winter, respectively. The examination of 2005 seasonal wind shows a high rate of the northwesterly wind in autumn and winter.
Seasonal wind along the Han river is predominant, and the wind moves along Jungrangcheon Stream and Tancheon Stream. The wind blowing along Jungrangcheon Stream meets valley winds formed in Mt. Dobongsan, Mt. Achasan and Mt. Suraksan, showing some vortex phenomenon in Sanggye-dong.
출처 : 서울특별시, 서울시 기후지도제작(1차년도), 2007