-
수도권
지형
-
지형
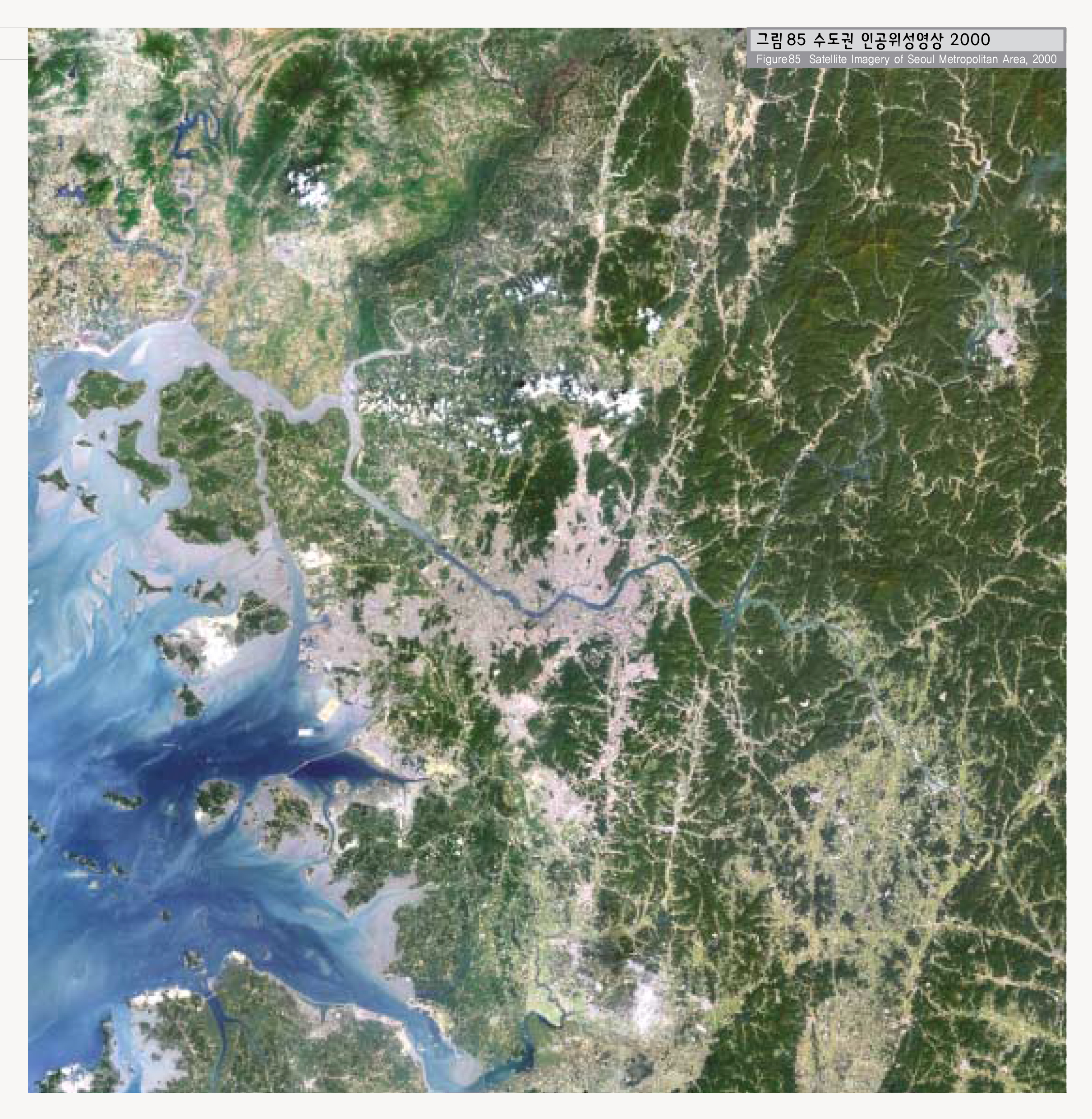
서울에 대한 이해를 위해서는 서울시 행정구역내의 특색 뿐 아니라 실질적 영향이 미치는 지역, 즉 광역차원에서의 수도권에 대한 이해가 필요하다. 수도권의 공간적 범위는 학자들마다 다르게 설정되기도 하나 본 책자에서는 경기도 행정구역내를 기준으로 살펴보았다.
경기도는 우리나라 중부의 서쪽에 위치하며, 서쪽에 황해의 경기만, 북서쪽에 황해도, 동쪽에 강원도, 남쪽에 충청도와 접하고 있으며, 도내에 서울특별시와 인천직할시가 있다. 황해도와의 경계선에는 마식령산맥, 충청북도와의 경계선에는 차령산맥이 달리고 있다.
경기도의 서부는 대체적으로 평탄한 충적평야이며, 기타지역은 산지인데 특히 동북부와 동부에는 고도 1,000m이상의 높은 산들도 솟아있으며, 가장 중요한 수계는 강원도에서 발원하는 한강수계이다.
Topography
To understand Seoul, an understanding of not only the characteristics of Seoul within its administrative sphere but the knowledge of the metropolitan broader perspectives to the regions where Seoul's influences reach, is needed. Each scholar has different ideas as to the spatial sphere of the Metropolitan area, however, for convenience' sake, this book regarded Kyonggido province as the Metropolitan areas.
Kyonggi-do is loated in the west of the middle region of Korea. It has Kyonggi bay in the west off the coast of the Yellow Sea, Hwanghae-do province to the northwest, Kangwon-do to the east, and Chungchong-do to the south, also Seoul city and Inchon Special City. Mts.Masingnyong on the border of Hwanghae-do and Mts. Charyong on the border of Chungchong bukdo run toward the west.
The west of Kyonggi-do is a level alluvial plains and other areas mountains, in particular northeast and eastern part of it lies high mountains of over 1,000m. The Hangang river originated from Kwangwon-do province is the main water supply source.
출처 : 국립지리원, 1997, 1;5000 수치지형도