-
환경
식생
-
식생
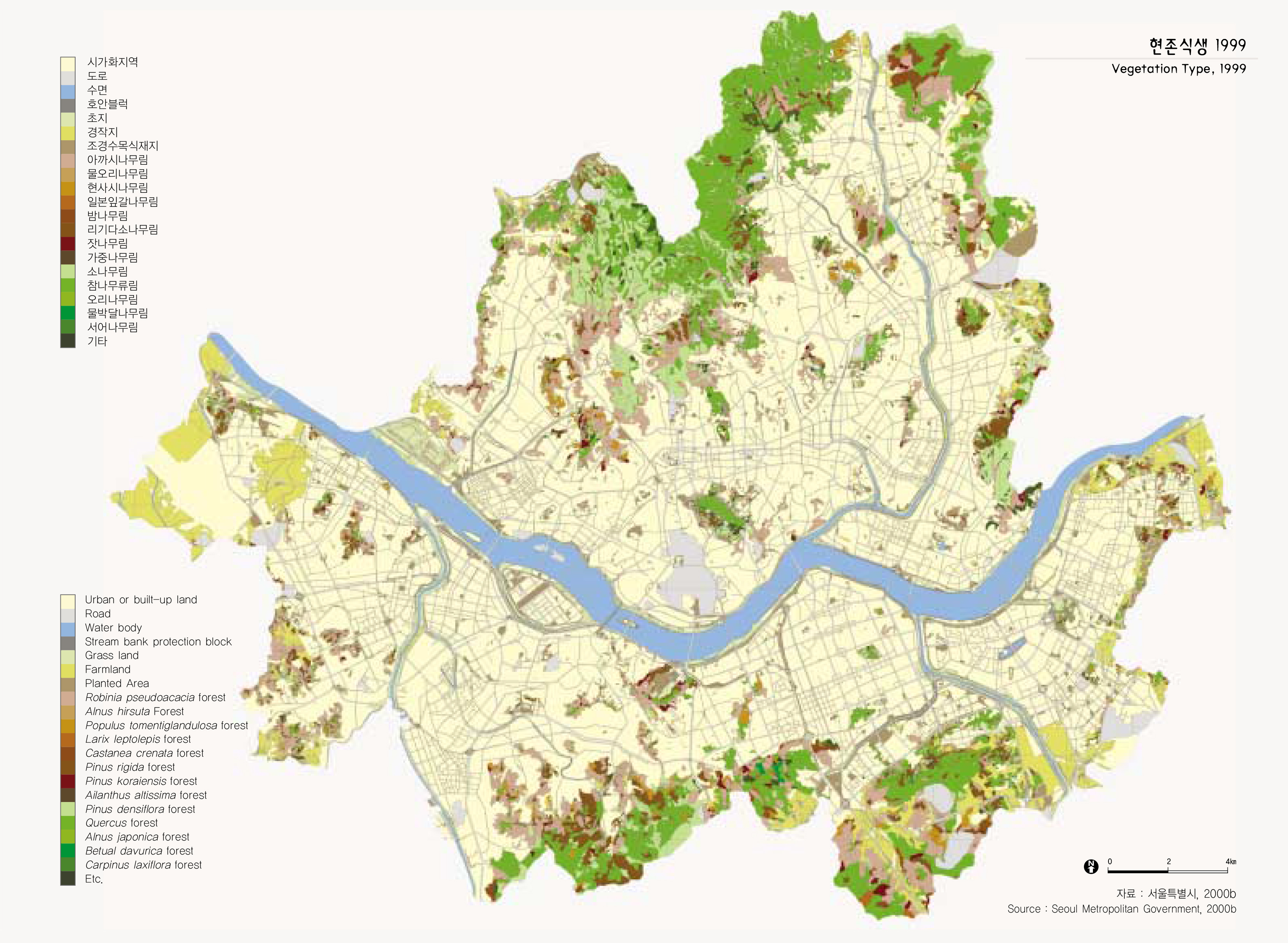
도시지역에 있어 식생현황은 야생동물의 서식지 확보 등 도시생태계 구성에 매우 중요한 기능을 담당한다. 서울시는 1999년 도시생태현황도를 제작하면서 서울시 전역에 대한 식생조사를 실시하였다.
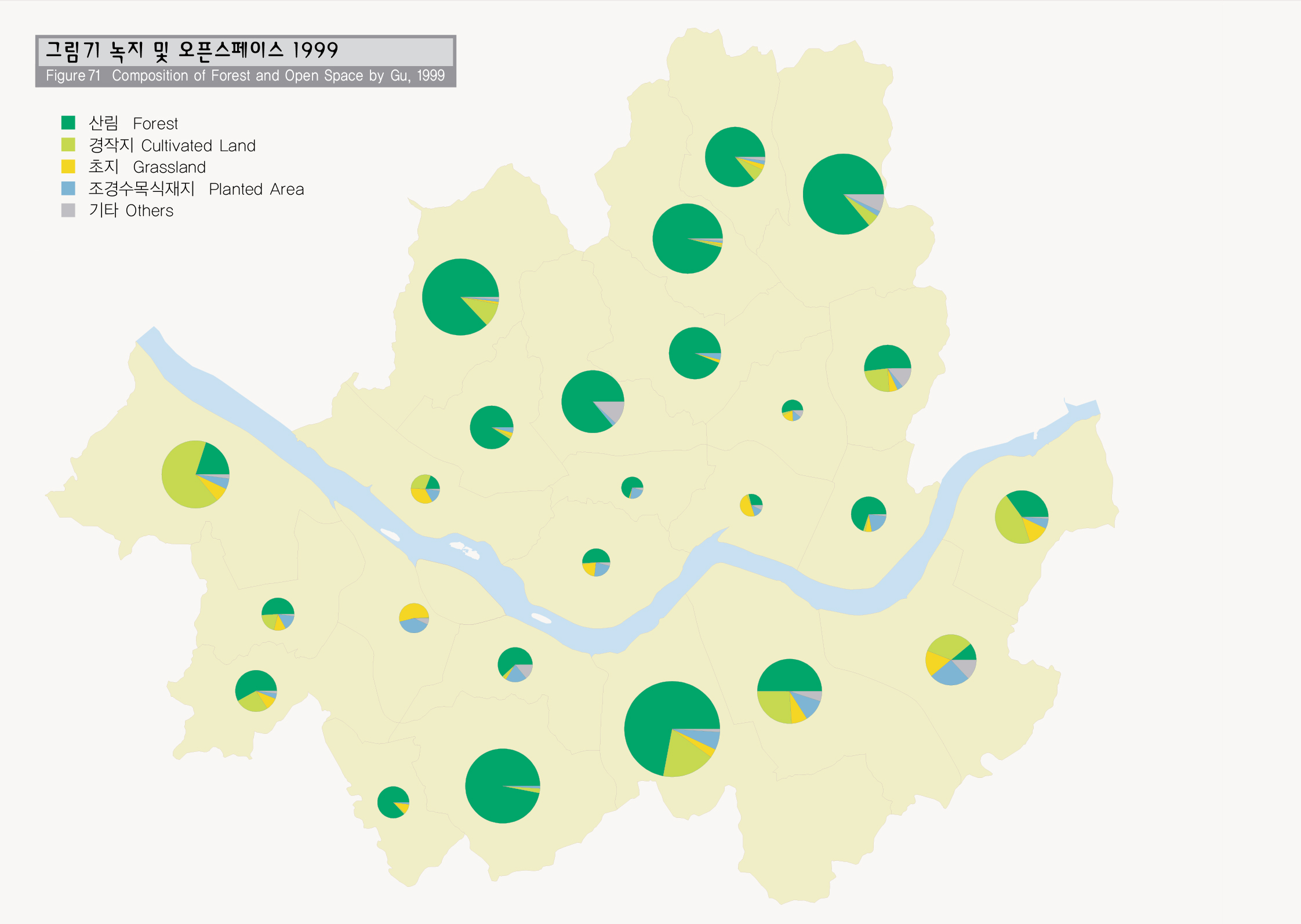
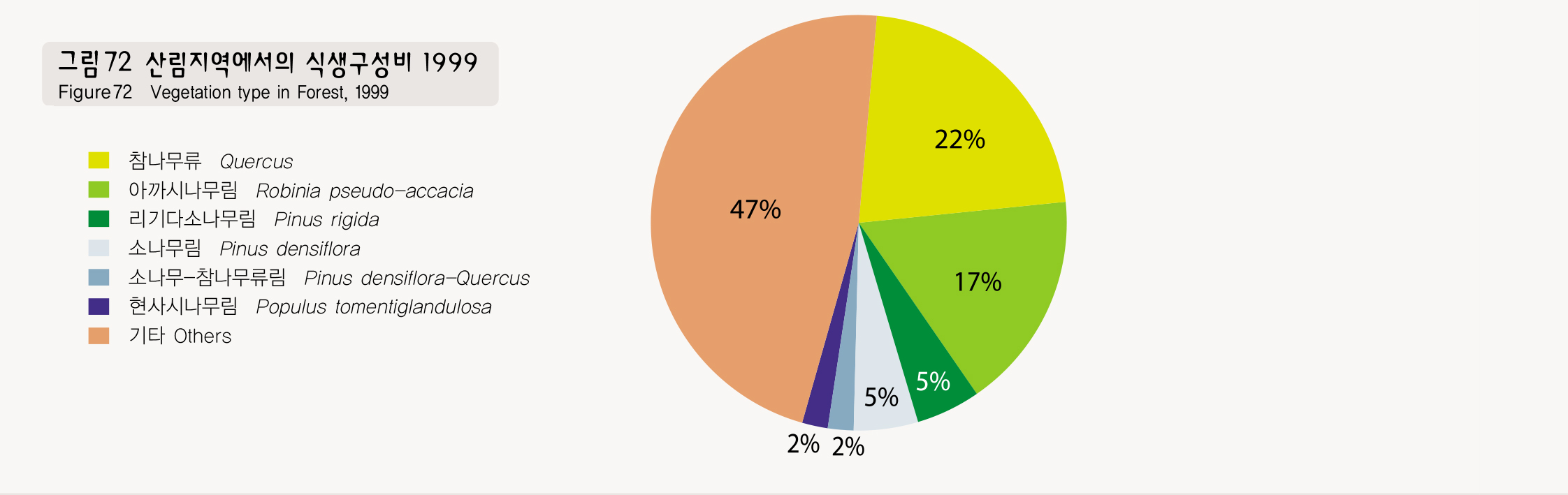
시가화 지역을 제외한 녹지 및 오픈스페이스 지역은 서울시 전체면적의 약 42%에 해당되는데, 이 가운데 산림지역이 전체면적의 26%로 가장 넓으며, 초지 및 수역이 9%, 경작지 5%, 기타 2.4%이다. 산림지역에서는 신갈나무, 졸참나무, 갈참나무 등 참나무류림이 서울시 전체의 22%로 가장 넓게 분포하고 있으며, 아카시나무림 17%, 리기다소 나무림 5%, 소나무림 5% 순으로 분포하고 있다.
초지 및 수역에서는 수면이 대부분이며, 귀화종 초본식생 지역이 우세하다. 경작지는 밭, 시설경작지, 논의 순으로 넓은 면적을 차지하고 있다.
Vegetation
Vegetation in urban regions plays a very important role in securing the habitats of wild animals and urban ecology. In 1999, Seoul conducted a comprehensive vegetation study across Seoul to draw up the Seoul Biotope Map. The study found that the forest and open space comprise 42% of the entire land of Seoul. Of them, forests take up 26%, the largest portion, while grassland and rivers, and wetland 9%, land under cultivation 5%, and others 2.4%. Of the forest regions, quercus forests including quercus mongolica, quercus aliena, and quercus serrata cover 22% of the land of Seoul, while the robinia pseudoacacia forests 17%, pinus rigida forests 5%, and pinus densiflora forests 5%.
Of the grassland, rivers and wetland region, watered area covers most of the region and grassland dominated by foreign species prevail. The land size under cultivation is in the order of dry-field farming, eqipped farmland, and rice farming.
출처 : 서울특별시, 2000b