-
주택유형
주택점유형태
-
주택점유형태
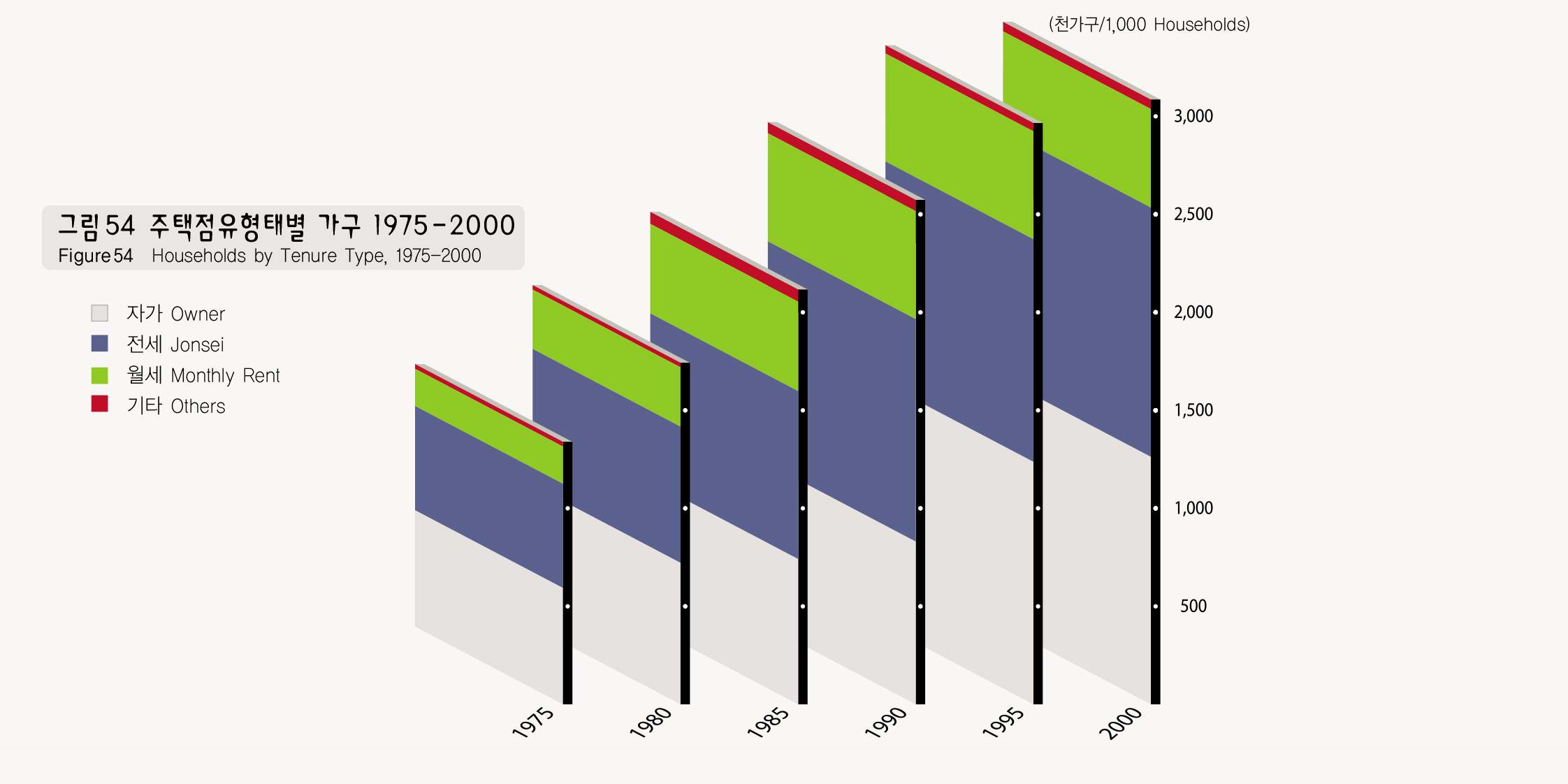
서울은 2000년에 자가가구비율이 41%, 전세 41%, 월세 16%로 1975년 이래 거의 유사한 패턴을 보이나 전∙월세가구 비율이 약간씩 증가하고 있는 추세이다. 주택점유형태는 주택유형과 밀접한 관련을 갖어 아파트가 우세한 지역에서는 자가가구가, 단독 및 다세대, 연립이 우세한 지역에서는 전세가구가 우세하다. 다만 도봉구 수유지역, 은평구 등은 연립 및 다세대 주택이 우세하나 점유형태로는 자가 가구가 우세하다. 월세가구가 우세한 지역은 단독세대가구가 많은 공단주변과 도심지로서 이동성이 많은 단독가구의 특성 때문이다. 서울은 대도시와 같은 슬럼현상은 나타나지 않고 있으나, 주택점유형태, 주택유형, 주택규모가 거주자 소득수준과 매우 높은 상관관계를 갖으며, 주택의 유형 및 점유형태 등에 따른 거주지 분리현상이 나타나고 있다.
Tenure Type
The tenure type of households in Seoul in 2000 was 41% owner households, 41% jonsei (rented housing on a deposit basis) households, and 16% monthly rent households, showing a similar pattern since 1975, but with some increases in both the jonsei and monthly payments households. The ownership of housing is closely related to housing types. For example, in the areas where there are many apartments, owner households are predominant, while there are more jonsei or monthly rent households are found in detached housing, row houses, and tenement housing areas. The Suyu area in Dobong-gu and Eunpyeong-gu are exceptions. Despite that tenement and multihousehold housing, there is predominantly owner households, which constitutes the majority in the region. Monthly rental households prevail around industrial complexes and downtown areas due to the high move out rates of the single-person household. Seoul does not have the slums that are often found in big cities. Ownership, housing patterns, and housing sizes are closely related to the income level of the residents and the separation of residential areas has become distinctive according to the housing type.
출처 : 통계청, 인구주택총조사 2000